
Download Center | Free Trial | C.O. Finder! | Telecom Databases | Traffic Finder! | Voice Over IP - VOIP | Number Portability! | Local Loop Finder! | Pricing and Ordering | Help/Support | Contact Us

|
|
Download Center | Free Trial | C.O. Finder! | Telecom Databases | Traffic Finder! | Voice Over IP - VOIP | Number Portability! | Local Loop Finder! | Pricing and Ordering | Help/Support | Contact Us |
TrafficFinder! TM - Erlang B Peaked Traffic Model - Neal Wilkinson
| Help Topics: |
Neal-Wilkinson Overflow Traffic Model |
|
Peaked Traffic (Neal-Wilkinson)
Traffic Models: Erlang B Peaked(Neal-Wilkinson)
Traffic Tables: |
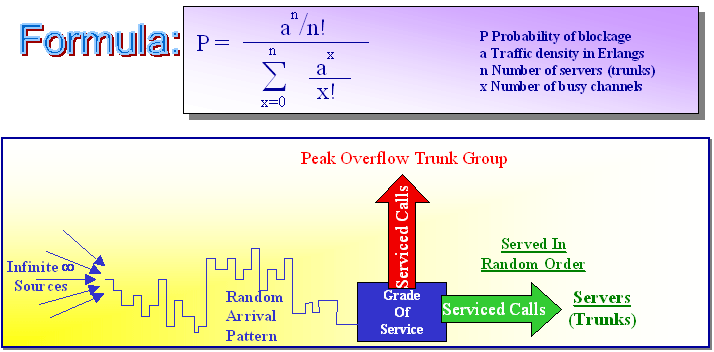 |
| The Neal-Wilkinson model is used to size overflow or alternate route trunk groups that receive peaked or bursty traffic from other high usage trunk groups such as inter-office backup paths. This model is useful when dealing with abnormally high traffic during occurrences such as holidays (Motherís Day) or disasters such as a stock market crash. The model uses the Erlang B formula but traffic is estimated using the equivalent random theory and peakedness factors. | |
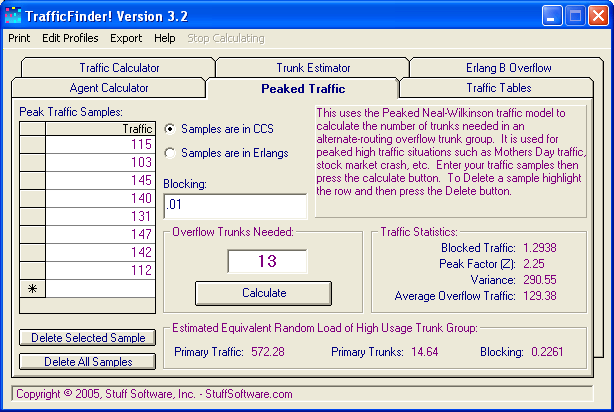
| Here's an example of the Neal-Wilkinson Peaked Traffic Model: | |
 |
|
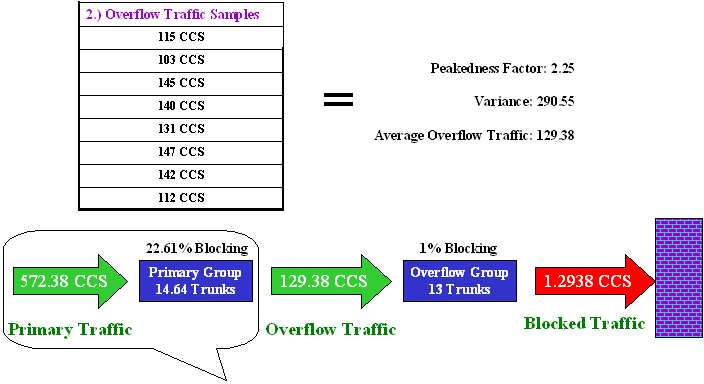
| You need to input 2 items: 1.) Desired blocking probablility and 2.) Overflow Traffic Samples. TrafficFinder! calculates the Peakedness Factor, Variance and Average Overflow Traffic. | |
 |
|
| Fictitious Primary Trunk Group (Equivalent Random Load) |